Benefit Preview (invitation only)
Wednesday, November 1, 5–9PM
Public Days
Thursday, November 2, 12–7PM
Friday, November 3, 12–7PM
Saturday, November 4, 12–7PM
Sunday, November 5, 12–5PM
Visit Michael Rosenfeld Gallery at Booth A4
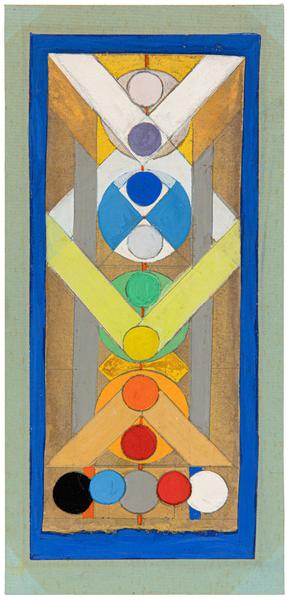
“Interior painting starts with the sign. In its initial states it is exorcism—a means of conquering the unknown. It is the oracle, the divination, the symbol of power, evolving from subjective states and moving towards their objective embodiments in a single plastic image.” [1]
—Charmion von Wiegand
Michael Rosenfeld Gallery is pleased to participate in The Art Show 2023 with Charmion von Wiegand, a solo exhibition of collages, paintings, and works on paper dating from 1945 to 1970, comprising a vibrant survey of the artist’s most productive years. The exhibition constitutes an abridged version of the Kunstmuseum Basel’s recent retrospective Charmion von Wiegand (March 24–August 8, 2023), to which the gallery loaned sixteen works.
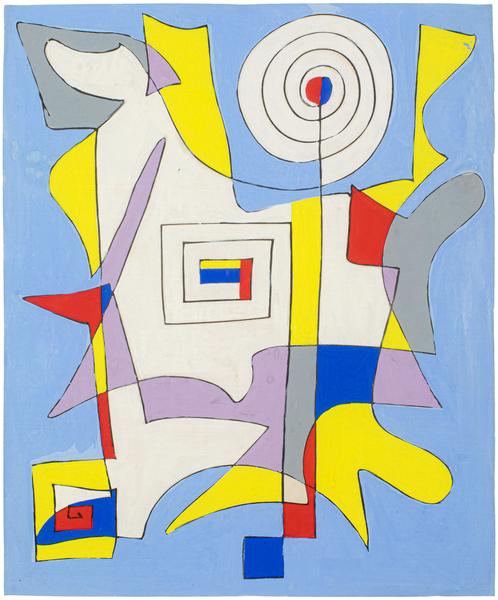
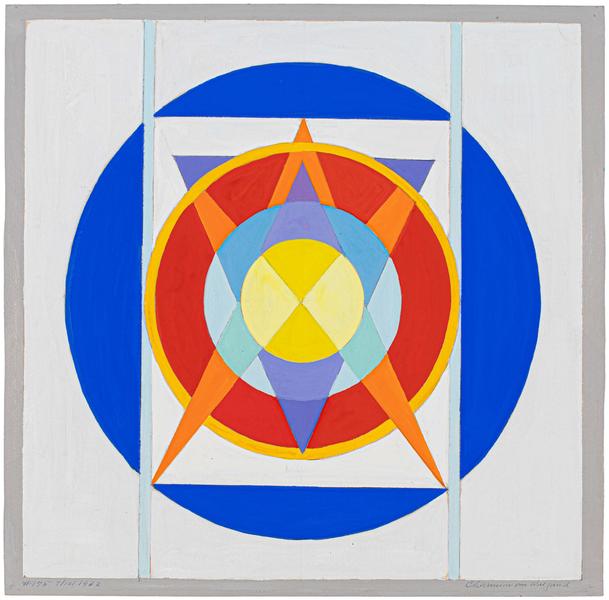
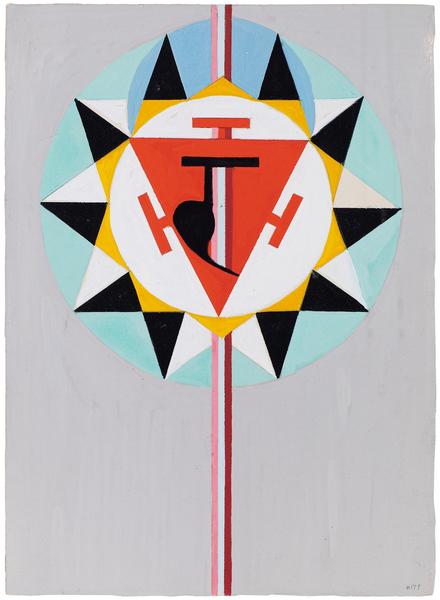
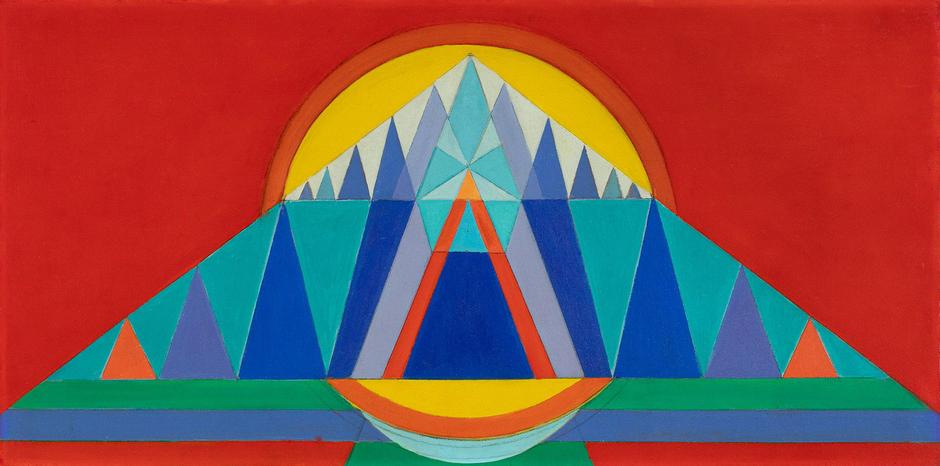
On view at Booth A4, Charmion von Wiegand charts the evolution of the artist’s mature style as she expanded her visual language to incorporate a thoroughly cosmopolitan range of influences. An important translator and protégé of Piet Mondrian (1872–1944), Charmion von Wiegand (1896–1983) developed her own approach to Neoplasticism that carried on the Dutch artist’s investigation of Theosophical principles while incorporating concepts, designs, and symbols from the Eastern religions she studied and eventually adopted as her personal spiritual guides. Also influenced by the automatist practices of the Surrealists and the densely urban environs of Manhattan, von Wiegand’s collages and biomorphic abstractions of the 1940s soon segued into a more overt embrace of Mondrian’s Neoplastic grid. She continued in this vein through the 1950s and gradually began to incorporate motifs and compositional processes drawn from Taoist doctrines. Throughout the 1960s, the artist’s intellectual interest and personal involvement in Eastern philosophies and religions, especially Tibetan Buddhism, inspired her to compose exacting amalgamations of stupas, mandalas, hexagrams, prismatic grids, and more.
Throughout her career, von Wiegand drew inspiration from a diverse range of sources, including Theosophist color theory, the I Ching, Egyptian cosmology, tantric yoga, and various branches of Buddhism, forging a singular language of geometric abstraction illuminated by her ardent pursuit of spiritual transcendence. From 1967 until her death in 1983, von Wiegand devoted her spiritual life to Mahayana Buddhism, and the art she produced in the years leading up to this conversion reflects her insatiable curiosity for non-Western systems of thought and spirituality. Scholar Massimo Introvigne, a sociologist of religion, posits that von Wiegand’s paintings of the 1960s “arguably represent the deepest Western visual representation of Tantrism: not a mere imitation of Eastern models, but a reinterpretation of the modern abstract art of the West through Tantric lenses.”[2] As art historians and curators continue to expand the history of spiritual abstraction in the 20th century to include such luminaries as Sonia Delaunay, Hilma af Klint, and Agnes Pelton, the work of Charmion von Wiegand has attracted greater institutional recognition and an international audience.
Mondrian had been active in Theosophical circles while living in Europe, and, in von Wiegand’s view, internalized the Theosophical doctrine to the extent where its teachings not only informed his painting practice but became “implicit to his life.”[3] Though her first exposure to Theosophy was in childhood, when she attended Theosophical Society meetings with her parents, von Wiegand did not study the subject in earnest until she was an adult. In the 1920s, she studied the esoteric philosophy of George Ivanovich Gurdjieff, who she came to revere as a spiritual guide, and her later friendship with Mondrian inspired her to revisit Theosophist thought; in 1946 she read the religion’s foundational text, The Secret Doctrine by Helena Blavatsky as well as ancillary texts by Annie Besant and C. W. Leadbeater, sparking an extended study of Theosophist color theory in her art. Another important event in von Wiegand’s spiritual life occurred in 1967, when she met Khyongla Rato Rinpoche, a Gelugpa monk who had recently arrived in New York as a refugee from China’s invasion of Tibet. Rato would mentor her spiritual study in the tradition of Mahayana Buddhism until her death, and it was through him that she was given an audience with the Dalai Lama during her travels to India and Tibet. In 1975, Rato founded the Tibet Center in New York and invited von Wiegand to sit on its Board of Advisors.